In today’s world, where sustainability and environmental consciousness are at the forefront of global discussions, the importance of energy efficiency in homes across Massachusetts and Rhode Island cannot be overstated. Not only does it play a pivotal role in reducing our carbon footprint, but it also offers New England homeowners tangible benefits, from significant cost savings on utility bills to enhancing the overall comfort of their living spaces.
Enter the HERS Rating. The Home Energy Rating System, commonly referred to as HERS, stands as a beacon in the realm of home energy performance. It’s not just another industry jargon; it’s a nationally recognized standard that provides a clear, quantifiable measure of a home’s energy efficiency. Much like how the MPG (Miles Per Gallon) rating gives car buyers an insight into a vehicle’s fuel efficiency, the HERS Rating offers homeowners and builders a glimpse into a home’s energy performance. The lower the HERS Index Score, the more energy-efficient the home is.
What is a HERS Rating?
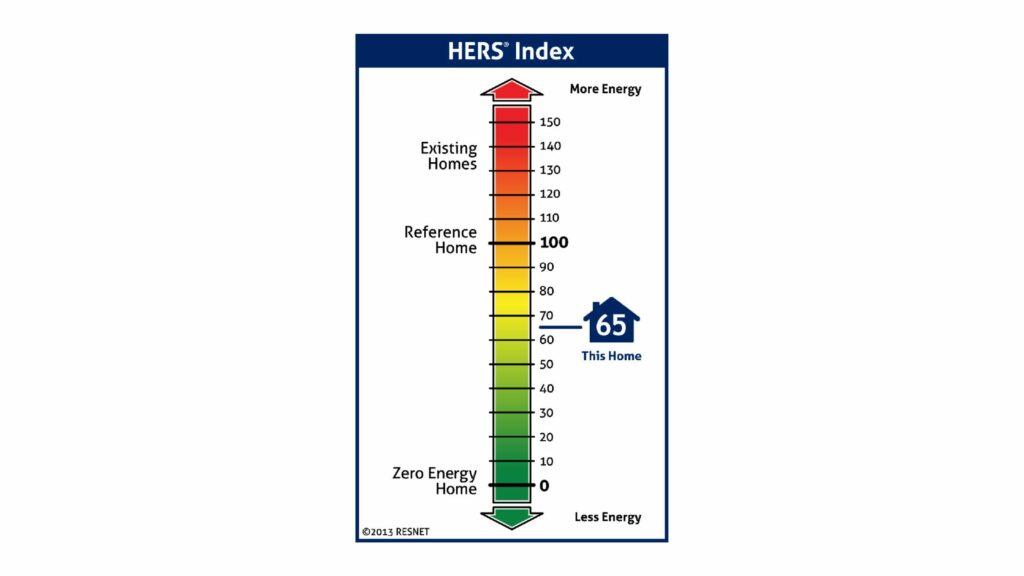
The Home Energy Rating System, or HERS, is a comprehensive assessment tool designed to evaluate a home’s energy efficiency. At its core, the HERS Rating provides a numerical representation known as the HERS Index Score, which indicates a home’s energy performance. The scale starts at 0, representing a net-zero energy home (a home that produces as much energy as it consumes), and can go upwards, with a higher score indicating less energy efficiency. For context, a typical resale home scores around 130 on the HERS Index, while a standard new home built to the latest code requirements is rated at around 100.
But how did the HERS Rating become the gold standard for energy performance in the building industry? The answer lies in its comprehensive approach and rigorous standards. Unlike other energy assessment tools, the HERS Rating evaluates all major energy-consuming systems in a home, including heating, cooling, lighting, appliances, and even water heating. This thoroughness ensures that homeowners and builders receive a holistic view of a home’s energy performance, allowing for informed decisions on improvements and investments.
The inception and widespread adoption of the HERS Rating can be attributed to the diligent efforts of the Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET). Founded in 1995, RESNET is a non-profit organization that has been instrumental in standardizing home energy efficiency ratings in the U.S. They developed the HERS Index as a means to provide a consistent, industry-recognized standard for measuring and comparing the energy performance of homes. Through their rigorous training and certification programs, RESNET ensures that HERS Raters are equipped with the knowledge and skills to accurately assess a home’s energy efficiency.
In essence, the HERS Rating, under the stewardship of RESNET, has transformed the way the building industry and homeowners perceive and prioritize energy efficiency. It’s not just a number; it’s a testament to a home’s commitment to sustainability, cost savings, and environmental responsibility.

How is a HERS Rating Determined?
Understanding the energy efficiency of a home is crucial in today’s environmentally-conscious world. But how exactly is a home’s energy performance measured and rated? Enter the HERS Rating, a comprehensive system that evaluates a home’s energy consumption and potential savings. Let’s delve into the process of how a HERS Rating is determined.
Inspection and Testing by Certified RESNET Home Energy Rater
The journey to obtaining a HERS Rating begins with a thorough inspection and testing of the home by a certified RESNET Home Energy Rater. These professionals undergo rigorous training and certification processes to ensure they can accurately assess a home’s energy performance. During the inspection, the rater examines various components of the home, including insulation levels, window efficiency, HVAC systems, and more. They also conduct specific tests, such as blower door tests to measure air leakage and duct tests to check for leakiness in the duct systems.
Significance of a Home’s HERS Rating in Relation to Its Energy Performance
Once the inspection and testing are complete, the data is analyzed to determine the home’s HERS Rating. This rating is a numerical representation of the home’s energy performance, with a lower score indicating better energy efficiency. For perspective, a home with a HERS Rating of 100 is considered to be built to standard energy code, while a home with a rating of 50 is 50% more energy-efficient than the standard new home.
Projected HERS Ratings vs. Official HERS Ratings
It’s essential to differentiate between projected and official HERS ratings. When designing a new home, builders can aim for a specific HERS rating. Using the home’s plans, an energy rater can model and estimate the likely HERS rating the home will achieve upon completion. This is known as the projected HERS rating. However, the official HERS rating is only determined after the home is built and has undergone the necessary RESNET certified inspections and tests. This ensures that the home’s actual energy performance aligns with the projected estimates, accounting for any discrepancies or changes made during construction.
What Does the HERS Index Score Represent?
The HERS Index Score is a measure of a home’s energy efficiency in comparison to a “reference home” built to the 2006 International Energy Conservation Code. The score quantifies how much energy the home is expected to consume compared to this standard reference. A lower HERS Index Score indicates a more energy-efficient home, while a higher score suggests less energy efficiency.
The Baseline Score of 100
The magic number in the HERS Index is 100. This score represents the energy consumption of the standard reference home. In essence, a home that scores 100 on the HERS Index is performing exactly in line with the 2006 energy code standards. It serves as a benchmark against which all other homes are compared.
Decoding Different Scores and Their Implications
150: A home with a HERS Index Score of 150 is 50% less energy efficient than the standard reference home. This means it consumes 50% more energy than a home built to the 2006 code standards. Such homes are typically older and haven’t benefited from modern energy-saving technologies or construction methods.
- 100: As mentioned, a score of 100 indicates that the home meets the energy performance of the reference home. It’s neither more nor less efficient than the 2006 standards.
- 50: A score of 50 signifies that the home is 50% more energy-efficient than the reference home. This could be due to a combination of high-quality insulation, energy-efficient windows, advanced HVAC systems, and other energy-saving measures.
- 0: Achieving a HERS Index Score of 0 means the home is a “net-zero energy” home. It produces as much energy (through renewable sources like solar panels or wind turbines) as it consumes, leading to a net energy consumption of zero.
- -10: A negative HERS Index Score, such as -10, indicates that the home produces more energy than it consumes. It’s not just a net-zero energy home; it’s a net-positive energy home. Such homes often have advanced renewable energy systems and are at the forefront of sustainable living.
A HERS Rating provides homeowners and builders with a clear, quantifiable measure of a home’s energy efficiency. By understanding how this rating is determined, individuals can make informed decisions about home construction, renovations, and energy-saving measures. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to reduce energy costs, a builder aiming to construct energy-efficient homes, or a buyer in the market for a green home, understanding the HERS Index Score is invaluable.

The Role of HERS Raters
In the world of home energy efficiency, HERS Raters play a pivotal role. They are the certified professionals who assess and determine the HERS Index Score of a home. Their expertise ensures that homeowners, builders, and potential buyers receive accurate and reliable information about a home’s energy performance. Let’s delve deeper into the responsibilities, certification process, and the importance of field verification and diagnostic testing in the work of a HERS Rater.
Definition and Responsibilities of a HERS Rater
A HERS Rater, or Home Energy Rating System Rater, is a trained and certified professional who evaluates a home’s energy efficiency. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Conducting on-site inspections to verify the construction and energy features of a home.
- Performing diagnostic tests, such as blower door tests and duct leakage tests, to assess the home’s energy performance.
- Using specialized software to analyze the collected data and calculate the home’s HERS Index Score.
- Providing recommendations to homeowners or builders on how to improve a home’s energy efficiency.
The Certification Process for Home Energy Raters
Becoming a HERS Rater isn’t a straightforward task. It requires rigorous training and certification to ensure that raters have the necessary knowledge and skills. The process typically involves:
- Completing a RESNET-accredited training program, which covers the principles of building science, energy modeling, and diagnostic testing.
- Passing the national RESNET test to demonstrate proficiency in the HERS rating process.
- Conducting supervised ratings under the guidance of a certified Quality Assurance Designee.
- Maintaining the certification through continuous education and periodic quality assurance reviews.
Significance of Field Verification and Diagnostic Testing
Field verification and diagnostic testing are the cornerstones of the HERS rating process. They ensure the accuracy and reliability of the HERS Index Score.
Field Verification: This involves a physical inspection of the home’s construction and energy features. It ensures that the home’s actual features match the data entered into the energy modeling software.
Diagnostic Testing: Diagnostic tests, such as blower door tests, measure the air tightness of a home. Duct leakage tests assess the efficiency of the HVAC system. These tests provide quantifiable data on the home’s energy performance, ensuring the HERS Index Score is based on real-world conditions.

The Impact of HERS Ratings on Home Buying and Selling
In today’s real estate market, energy efficiency is not just a buzzword—it’s a significant factor that can influence the buying and selling decisions of homeowners and potential buyers alike. The HERS Rating, with its comprehensive assessment of a home’s energy performance, has become an essential tool in this context. Let’s explore how HERS ratings are shaping the dynamics of the real estate market.
How HERS Ratings Influence the Resale Price of Homes
A favorable HERS rating can be a strong selling point for homeowners. Homes with lower HERS scores, indicating higher energy efficiency, often command higher resale prices. Here’s why:
Cost Savings: A more energy-efficient home translates to lower utility bills. Over time, these savings can be substantial, making homes with better HERS scores more attractive to potential buyers.
Future-Proofing: As energy costs rise and environmental concerns become more pressing, homes with good HERS ratings are seen as better long-term investments. They’re designed to be more resilient against future energy price hikes.
Comfort: Energy-efficient homes often offer a more comfortable living environment. They maintain consistent temperatures, have fewer drafts, and offer better indoor air quality. This enhanced living experience can be a significant draw for buyers.
The Growing Trend of Including HERS Scores in MLS Listings
Multiple Listing Services (MLS) are increasingly recognizing the importance of energy efficiency in the home buying process. As a result, many MLS platforms now include fields for HERS scores. This trend offers several benefits:
- Transparency: By including HERS scores in listings, sellers can provide clear evidence of their home’s energy performance, making it easier for buyers to compare homes based on energy efficiency.
- Increased Visibility: Homes with impressive HERS scores can stand out in listings, attracting more potential buyers and possibly leading to quicker sales.
- Informed Decisions: For buyers, having access to HERS scores means they can make more informed decisions, factoring in potential energy costs and the comfort of living in an energy-efficient home.
The Importance of Energy Efficiency for Potential Homebuyers
For many modern homebuyers, energy efficiency is a top priority. Here’s why:
- Environmental Concerns: As awareness of environmental issues grows, many buyers are looking for homes that have a smaller carbon footprint. A good HERS score is an indication of a home’s environmental friendliness.
- Economic Considerations: With rising energy prices, potential buyers are keen on finding homes that promise lower utility bills.
- Quality of Construction: A low HERS score often indicates a home built with attention to detail, using quality materials and modern construction techniques. For buyers, this can be a sign of a well-constructed, durable home.

HERS Ratings in Rhode Island and Massachusetts
The Northeastern states of Rhode Island and Massachusetts, with their rich history and commitment to sustainability, have been at the forefront of adopting energy efficiency measures. The HERS rating system, as a measure of a home’s energy performance, plays a pivotal role in both states’ residential construction landscape. However, there are nuances in how each state approaches HERS ratings. Let’s delve into the specifics of HERS ratings in Rhode Island and Massachusetts.
Differences in HERS Rating Requirements Between the Two States
While both Rhode Island and Massachusetts recognize the importance of HERS ratings, there are subtle differences in their requirements:
- Thresholds and Standards: Massachusetts has historically set more stringent energy efficiency standards, which often translates to a stricter threshold for HERS ratings compared to Rhode Island. Builders in Massachusetts might find themselves needing to achieve a lower HERS score to meet state requirements than their counterparts in Rhode Island.
- Incentive Programs: Both states offer incentive programs for energy-efficient construction, but the specifics of these programs and the role of HERS ratings within them can vary. For instance, certain rebates or tax incentives might be tied to achieving a specific HERS score.
The Changing Landscape of HERS Rating Requirements in Massachusetts for 2023 and Beyond
Massachusetts is known for its progressive stance on environmental issues, and this extends to its building codes and standards. As we move into 2023 and beyond:
- Stricter Standards: The state is expected to introduce even more rigorous energy efficiency standards. This could mean a further lowering of the acceptable HERS score for new constructions.
- Integration with Other Green Building Standards: Massachusetts is looking at a holistic approach to sustainable construction. This means HERS ratings might be considered alongside other green building certifications, creating a comprehensive view of a building’s environmental impact.
- Passing HERS Rating Score in Massachusetts: A HERS Rating in Massachusetts compares a home to be built with a user-defined reference home with similar characteristics. The scale used is 0 to 100, with lower numbers indicating better energy efficiency. As of 2022, a HERS Rating score of 55 is required. However, this requirement will drop to 52 starting January 1st, 2023. By 2024, the score will see a significant reduction, dropping by 10 points to 42.
Rhode Island’s Residential New Construction Program and Its Implications for HERS Ratings
Rhode Island’s Residential New Construction program is a testament to the state’s commitment to energy-efficient homes. Here’s how it intersects with HERS ratings:
- Mandatory HERS Ratings: For homes to qualify under this program, they need to undergo a HERS rating assessment. This ensures that new constructions adhere to the state’s energy efficiency standards.
- Incentives for Lower Scores: The program offers incentives for homes that achieve particularly low HERS scores. This not only promotes the construction of energy-efficient homes but also makes them more attractive to potential buyers.
- Training and Certification: Recognizing the importance of accurate HERS assessments, Rhode Island has invested in training and certifying more HERS raters. This ensures that the ratings are consistent and reliable.

Practical Steps for Builders and Homeowners in Massachusetts and Rhode Island
Achieving an optimal HERS rating is not just about ticking boxes on a checklist; it’s about understanding the intricacies of home construction and the factors that influence energy efficiency. For builders and homeowners in Massachusetts and Rhode Island, where energy standards are progressively becoming more stringent, planning and knowledge are key. Here are some practical steps to ensure a successful HERS rating:
1. Early Planning is Essential
Engage Early with a HERS Rater: Before breaking ground, consult with a certified HERS Rater. Their insights can guide the design and construction process, ensuring that energy efficiency is integrated from the outset.
Understand Local Requirements: Both Massachusetts and Rhode Island have specific energy standards and requirements. Familiarize yourself with these to ensure compliance and to take advantage of any available incentives.
2. Prioritize the Thermal Envelope
Insulation: Proper insulation is crucial. It prevents heat transfer, keeping homes warm in the winter and cool in the summer. Ensure that insulation is consistently applied throughout the home, paying special attention to attics, basements, and exterior walls.
Air Sealing: Gaps and cracks can be major sources of energy loss. Invest in comprehensive air sealing to prevent drafts and ensure a comfortable indoor environment.
3. Invest in Efficient HVAC Equipment
Choose the Right System: Not all HVAC systems are created equal. Opt for energy-efficient models that are appropriately sized for the space. An oversized or undersized system can lead to inefficiencies and increased energy consumption.
Regular Maintenance: Even the best HVAC systems can lose efficiency over time. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity.
4. Consider Other Influential Factors
Windows and Doors: Energy-efficient windows and doors can significantly reduce heat loss. Look for products with a good U-value and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC).
Orientation and Design: The way a home is oriented can influence its energy consumption. For instance, maximizing southern exposure can take advantage of passive solar heating.
5. Recommendations for Improving a Home’s HERS Score
Upgrade Appliances: Energy-efficient appliances, from refrigerators to washing machines, can make a significant difference in a home’s energy consumption. Look for ENERGY STAR-rated products.
Renewable Energy: Consider integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines. These can not only improve the HERS score but also lead to long-term energy savings.
Continuous Learning: Energy efficiency is a rapidly evolving field. Stay updated with the latest technologies, materials, and best practices to continually improve and adapt.

Available Incentives and Rebates
In the pursuit of a more sustainable and energy-efficient future, both Rhode Island and Massachusetts have rolled out a series of incentives and rebates to encourage homeowners and builders to adopt energy-saving measures. These programs not only help in reducing the carbon footprint but also offer financial benefits, making energy-efficient upgrades more accessible and appealing.
Massachusetts: The Mass Save Program
Mass Save is a collaborative initiative in Massachusetts, backed by the state’s leading utility and energy providers. The program offers:
Rebates on Energy-Efficient Appliances: Homeowners can get rebates on ENERGY STAR certified appliances, which can lead to significant savings on utility bills in the long run.
- Incentives for Home Insulation: Proper insulation is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment and reducing energy consumption. Mass Save provides incentives for homeowners who upgrade their insulation.
- Home Energy Assessments: Before diving into renovations, homeowners can benefit from a no-cost home energy assessment. This assessment identifies areas of improvement and provides recommendations tailored to the specific needs of the home.
- Financing Options: For those looking to make larger energy-efficient upgrades, Mass Save offers 0% financing on approved energy-saving projects.
Rhode Island: The EnergyWise Program
EnergyWise is Rhode Island’s answer to promoting energy efficiency among its residents. The program provides:
Rebates on Heating and Cooling Systems: Upgrading to an energy-efficient heating or cooling system can be a significant investment. Energy Wise offers rebates to offset these costs, making it more affordable for homeowners.
- Incentives for Home Weatherization: Weatherizing a home can lead to substantial energy savings. The program provides incentives for measures like air sealing and insulation.
- Energy Audits: Similar to Massachusetts, Rhode Island offers energy audits to help homeowners identify areas of improvement. These audits provide a roadmap for energy-efficient upgrades.
- Discounts on LED Lighting: Switching to LED lighting is one of the simplest ways to reduce energy consumption. Energy Wise offers discounts on LED bulbs, making the switch even more cost-effective.
How to Take Advantage of These Programs
- Stay Informed: Both programs frequently update their offerings. Regularly checking their official websites or subscribing to their newsletters can keep you updated on the latest incentives.
- Consult with Professionals: Engaging with a certified energy auditor or a HERS Rater can provide insights into the most beneficial upgrades for your specific situation.
- Plan Ahead: If you’re building a new home or planning a renovation, factor in these incentives from the start. This proactive approach ensures you maximize the benefits.
In conclusion, both Massachusetts and Rhode Island offer robust programs to support energy efficiency. By leveraging the Mass Save and Energy Wise programs, homeowners and builders can make impactful energy-efficient upgrades while enjoying financial benefits.

Embracing HERS Ratings: A Brighter Future for Rhode Island and Massachusetts Homeowners and Builders
In the context of global sustainability efforts, Massachusetts and Rhode Island have emerged as frontrunners in championing energy efficiency. The Home Energy Rating System (HERS) plays a pivotal role in this movement, guiding homeowners and builders in these states towards more sustainable and energy-efficient practices.
The HERS ratings, deeply embedded in the building culture of Massachusetts and Rhode Island, are not mere numbers. They symbolize a commitment to a greener future, a dedication to reducing our carbon footprint, and a collective effort to ensure a sustainable environment for the generations to come. As homeowners and builders in these states, understanding and leveraging the HERS Index is not just beneficial—it’s imperative.
For residents of Massachusetts and Rhode Island, a commendable HERS rating means more than just reduced energy bills. It signifies a home that aligns with the region’s sustainability goals, offering a comfortable living environment that’s in harmony with nature. Builders, on the other hand, find in the HERS rating a valuable tool that not only adds merit to their projects but also resonates with an audience that’s increasingly environmentally conscious.

HERS Rating: Join the Green Revolution with Energy Geeks
In wrapping up, it’s evident that as Massachusetts and Rhode Island continue their journey towards a more sustainable future, the HERS rating system will be at the forefront of this transformation. If you’re a resident of these states and are keen on minimizing energy consumption, maximizing savings, and ensuring comfort throughout the year, then Energy Geeks is here to assist. Our mission is to provide the most comprehensive and efficient solutions to reduce energy use in your home. Reach out to us and be a part of this green revolution.